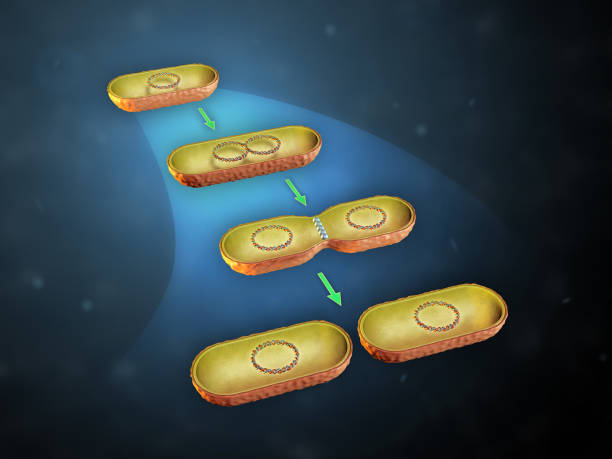
Bacteria binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction that involves a single parent organism splitting into two daughter cells. During binary fission, the bacterium’s single circular chromosome is replicated, and the two copies are attached to different parts of the cell membrane. The cell then elongates and eventually splits into two daughter cells, each with its own copy of the chromosome. The process is repeated as the daughter cells divide, creating a chain of identical cells.
Bacteria,Binary Fission,Cell
