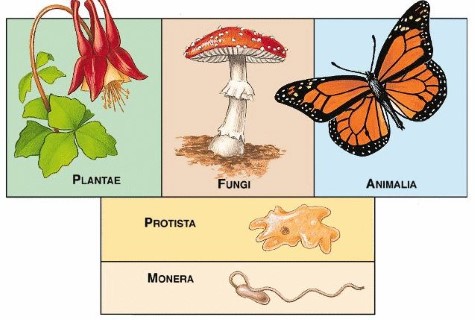
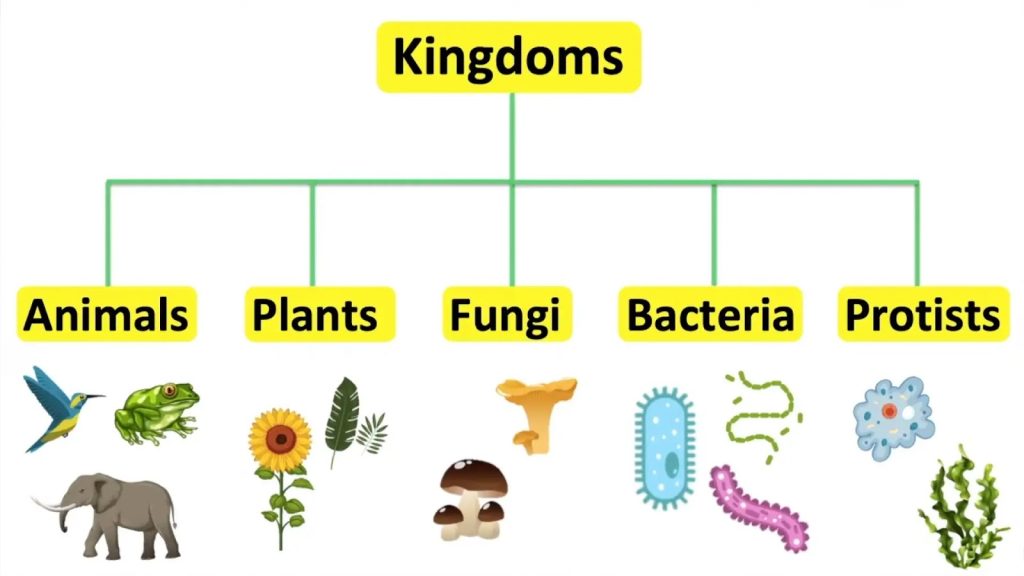
The five-kingdom classification system is a widely accepted system of classifying living organisms into five distinct kingdoms. This system was developed by Robert Whittaker in 1969 and is based on the shared characteristics of organisms. The five kingdoms are: Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia.
Monera: Monera is the kingdom of single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus. These organisms are also known as prokaryotes and include bacteria and blue-green algae.
Protista: The kingdom Protista consists of mostly unicellular organisms that have a nucleus, such as protozoa, diatoms, and some algae.
Fungi: The kingdom Fungi consists of organisms such as mushrooms, molds, and yeasts. These organisms are multi-cellular and lack chlorophyll.
Plantae: The kingdom Plantae consists of multi-cellular organisms that are autotrophic, meaning that they can produce their own food through photosynthesis. Plants have cell walls and include trees, shrubs, and herbs.
Animalia: The kingdom Animalia consists of multi-cellular organisms that are heterotrophic, meaning they must obtain their food from other sources. Animals have no cell walls and include mammals, reptiles, birds, fish, and other invertebrates.
The five-kingdom classification system is the most widely accepted system of classifying living organisms. It is based on the shared characteristics of the five kingdoms and is used to group organisms into their respective kingdoms.
five-kingdom classification system,
Robert Whittaker,
Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia.
