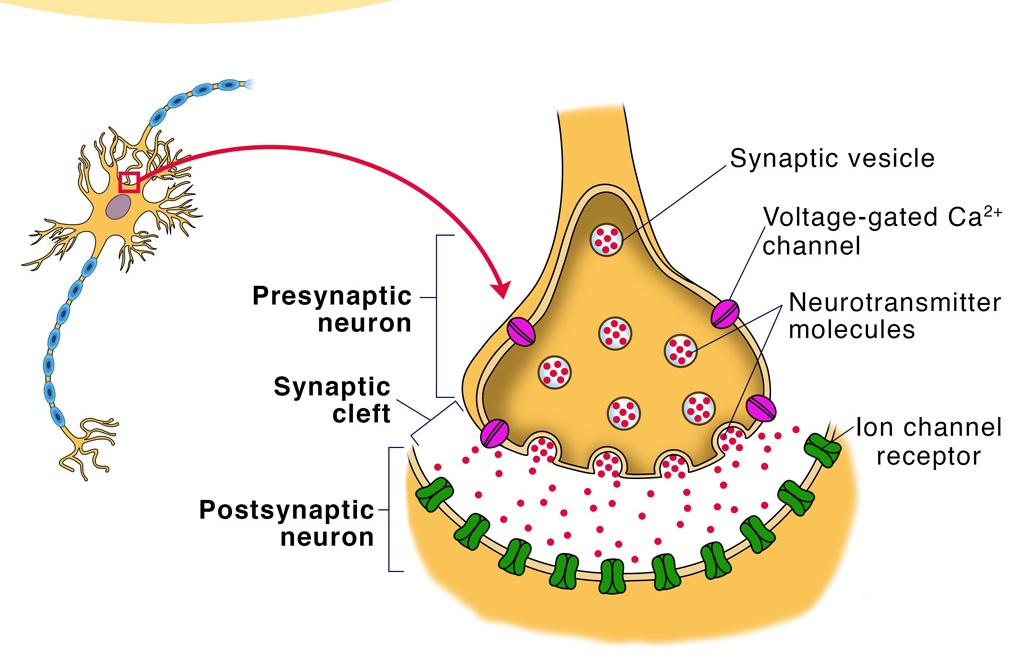
The structure of a synapse consists of three parts: a presynaptic terminal, a postsynaptic terminal, and the synaptic cleft. The presynaptic terminal contains neurotransmitter-filled vesicles, while the postsynaptic terminal contains receptor proteins that bind to neurotransmitter molecules released by the presynaptic terminal. The synaptic cleft is the gap between the presynaptic and postsynaptic terminals, and is filled with a fluid containing chemicals that can bind to the neurotransmitters released by the presynaptic terminal.
postsynaptic terminal,
neurotransmitter-filled vesicles
