The hypothalamus and the pituitary gland have a close relationship and work together to regulate the body’s hormones. The hypothalamus is responsible for producing hormones that control the release of other hormones from the pituitary gland. These hormones from the hypothalamus are sent to the pituitary gland, which then releases a range of other hormones into the bloodstream. This process is known as the hypothalamic-pituitary-axis and is responsible for regulating a range of processes in the body, including growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
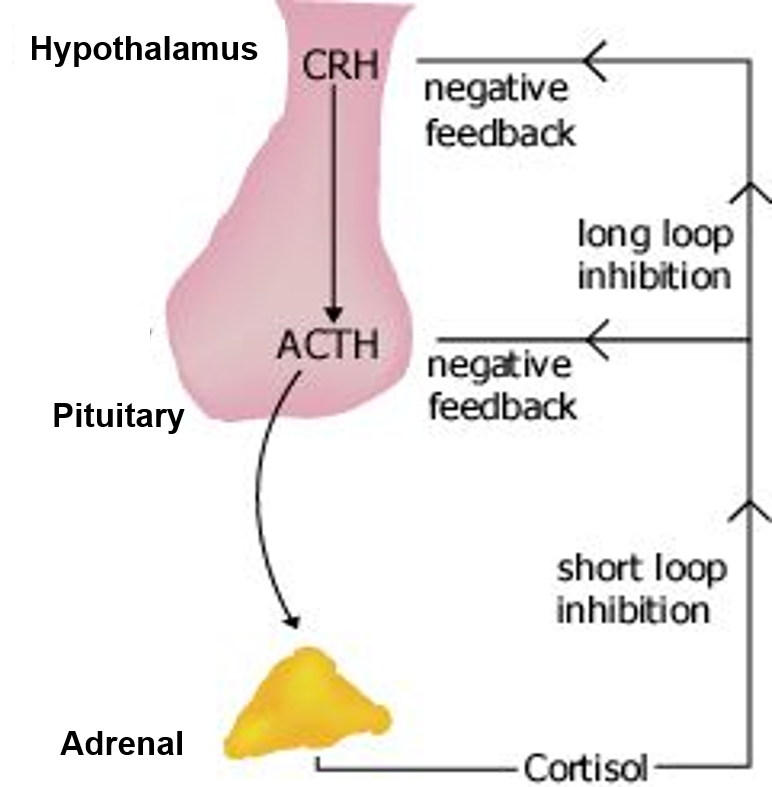
The hypothalamus and pituitary gland have an important relationship. The hypothalamus produces hormones called releasing factors, which control hormone production in the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus produces three releasing factors: thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), and corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH). TRH stimulates the pituitary gland to produce thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which in turn stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones. GnRH stimulates the pituitary gland to produce gonadotropins, which control the production of the reproductive hormones estrogen and testosterone. CRH stimulates the pituitary gland to produce adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which stimulates the adrenal glands to produce cortisol, the primary stress hormone.
The hypothalamus and the pituitary gland are two important components of the endocrine system. The hypothalamus is a small structure located in the brain and is responsible for controlling the release of hormones from the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland is a small structure located at the base of the brain and produces hormones that regulate various functions in the body such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction.The hypothalamus and pituitary gland work together to maintain homeostasis by controlling the release of hormones into the bloodstream. The hypothalamus detects changes in the body’s environment and sends signals to the pituitary gland to release the appropriate hormones. The pituitary gland then releases the hormones to the target organs, which in turn respond by carrying out the necessary changes or functions. This process is known as the hypothalamo-pituitary-endocrine system.
The hypothalamus is an integral part of the endocrine system and plays an essential role in the regulation of the pituitary gland, the primary endocrine gland. The hypothalamus produces and secretes hormones that directly affect the pituitary gland, which then releases hormones that act on other endocrine glands, such as the thyroid and adrenal glands. The hypothalamus is responsible for the release of hormones that regulate the body’s homeostatic functions, including metabolism, body temperature, and reproductive cycles. Hypothalamic hormones also influence the endocrine function of the pituitary gland by stimulating the release of hormones, such as growth hormone and prolactin. These hormones, in turn, act on other endocrine glands to regulate the body’s metabolic processes and reproductive functions.
hipothalamus, pitutary
