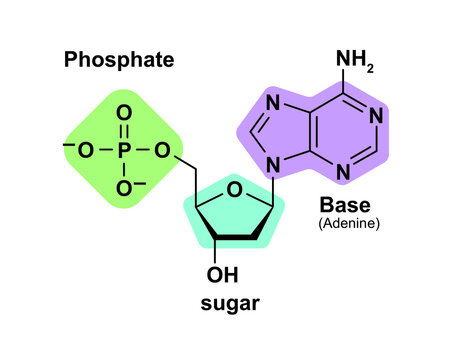
A nucleotide is a subunit of DNA or RNA and is composed of three parts: a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose in the case of DNA or ribose in the case of RNA), a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group. There are four different types of nucleotides in DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C).A nucleotide is composed of three components: a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose or ribose), and a phosphate group. The nitrogenous base can be either adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), or thymine (T) in DNA or adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), uracil (U) in RNA. The five-carbon sugar is always either deoxyribose or ribose. Finally, the phosphate group is composed of one phosphate molecule and two oxygen atoms.
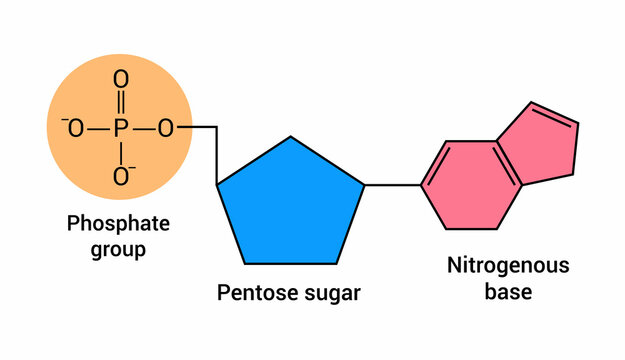
Nucliotide
