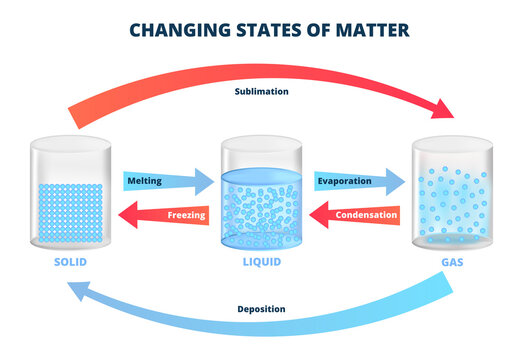
When a substance is heated, its state changes. For example, when water is heated, it changes from a liquid to a gas (water vapour). As the temperature increases, the molecules of the substance gain more energy and move faster and faster. Eventually, the molecules move so quickly that they escape the attraction of the other molecules and form a gas.
Energy of the particles
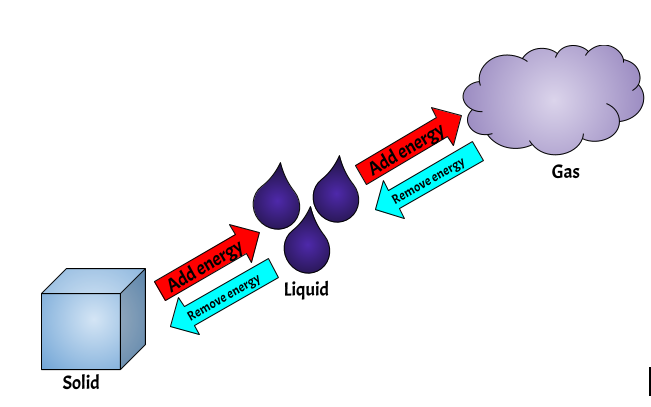
Particles in a solid state have the least amount of energy as they are in a fixed position and may not move. Particles in a liquid state have more energy as they are able to move around freely. Particles in a gaseous state have the most energy as they are free to move in any direction.
Distance between particles
The distance between particles during a change of state in a simple substance depends on the specific substance and its temperature. Generally, as the temperature increases, the distance between particles will decrease as the particles move faster and have less space to move around. At the point of change of state, the particles will be closest together. For example, when a liquid is heated and reaches its boiling point, the particles are at their closest point and the liquid starts to turn into a gas.
Attraction between particles
When particles change their state, they are attracted to other particles in the same state. For example, when a liquid turns to a gas, the gas molecules will be attracted to other gas molecules, and the liquid molecules will be attracted to other liquid molecules. The attraction between the particles is known as intermolecular forces.
Movement of particles
When a substance changes from one state to another, the particles of the substance move. For example, when a solid changes to a liquid, the particles move closer together and become more organized. When a liquid changes to a gas, the particles move further apart and become more chaotic.
