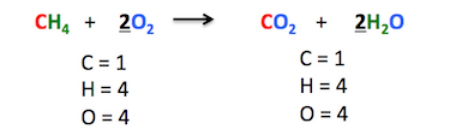
Balanced chemical equations are equations that show the chemical reactants and products on either side of the equation in equal amounts. In other words, the number of atoms of each element must be equal on both sides of the equation.
For example, the reaction of hydrogen and oxygen to form water can be written as:
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
This equation is already balanced, since there are two atoms of hydrogen on the left side, and two atoms of hydrogen on the right side. There are two atoms of oxygen on the left side, and two atoms of oxygen on the right side.
