
Corrosion is the gradual destruction of material, usually metals, by chemical reaction with its environment. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metals in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen.
Rusting of iron experiment
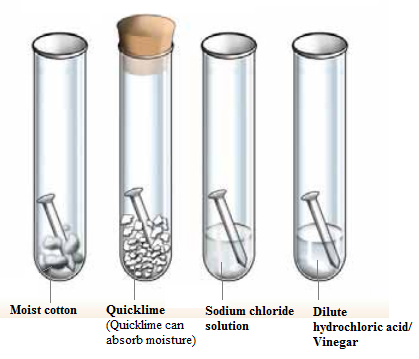
- Fill four test tubes with water.
- Place an iron nail in each test tube and label each one.
- Place one test tube in a dark cupboard for two weeks, one in the refrigerator for two weeks, one in direct sunlight for two weeks and one outside for two weeks.
- After two weeks, remove the test tubes and examine the nails.
- Compare the results and note any changes in the nails.
- Take pictures of the nails for further comparison.
- Draw conclusions about the rusting process based on the results.
Test Tube 1: The iron nail is not corroded and remains unchanged.
Test Tube 2: The iron nail has begun to rust and has a light orange hue.
Test Tube 3: The iron nail is heavily corroded and has a dark orange hue.
Test Tube 4: The iron nail is completely corroded and has a black hue.
Conclusion: The experiment shows that iron nails corrode more rapidly when exposed to a combination of water and oxygen. The longer the nail is exposed to this combination, the more heavily corroded it becomes.
