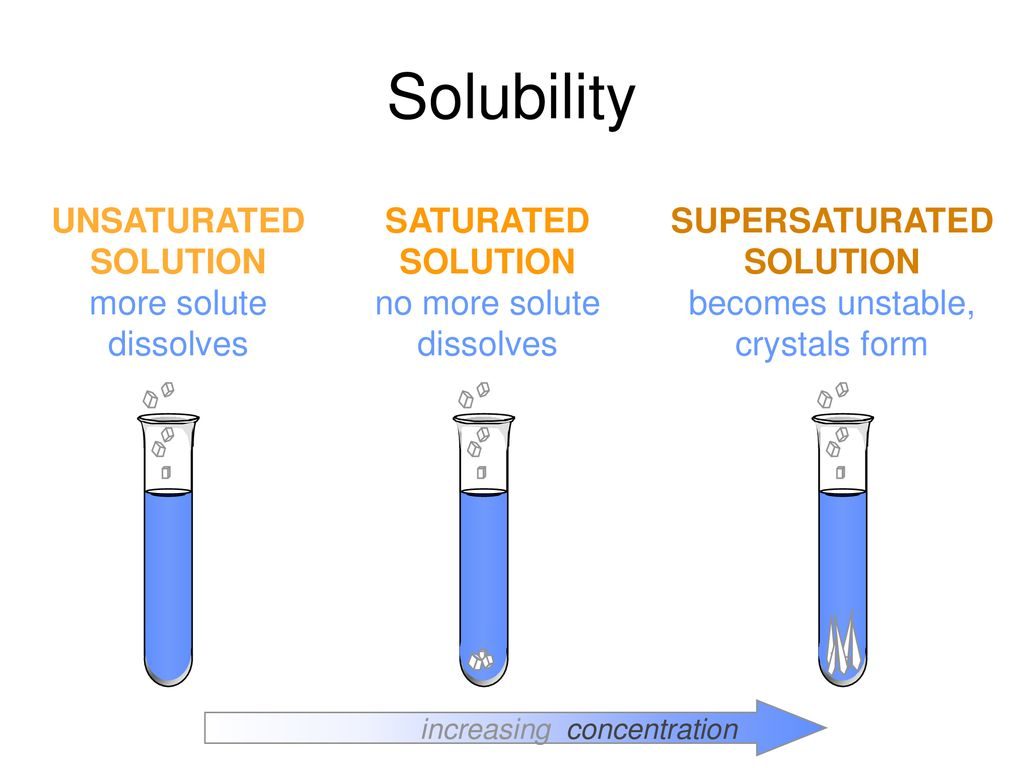
Super saturation is a term used to describe a solution that contains a higher solute concentration than is able to be held in the solvent. This means that the solution is in a state of imbalance and that the solute is likely to precipitate out of the solution. A common example of super saturation is when sugar is dissolved in water. If too much sugar is added to the water, it can no longer be dissolved, and the excess sugar will settle at the bottom of the container.