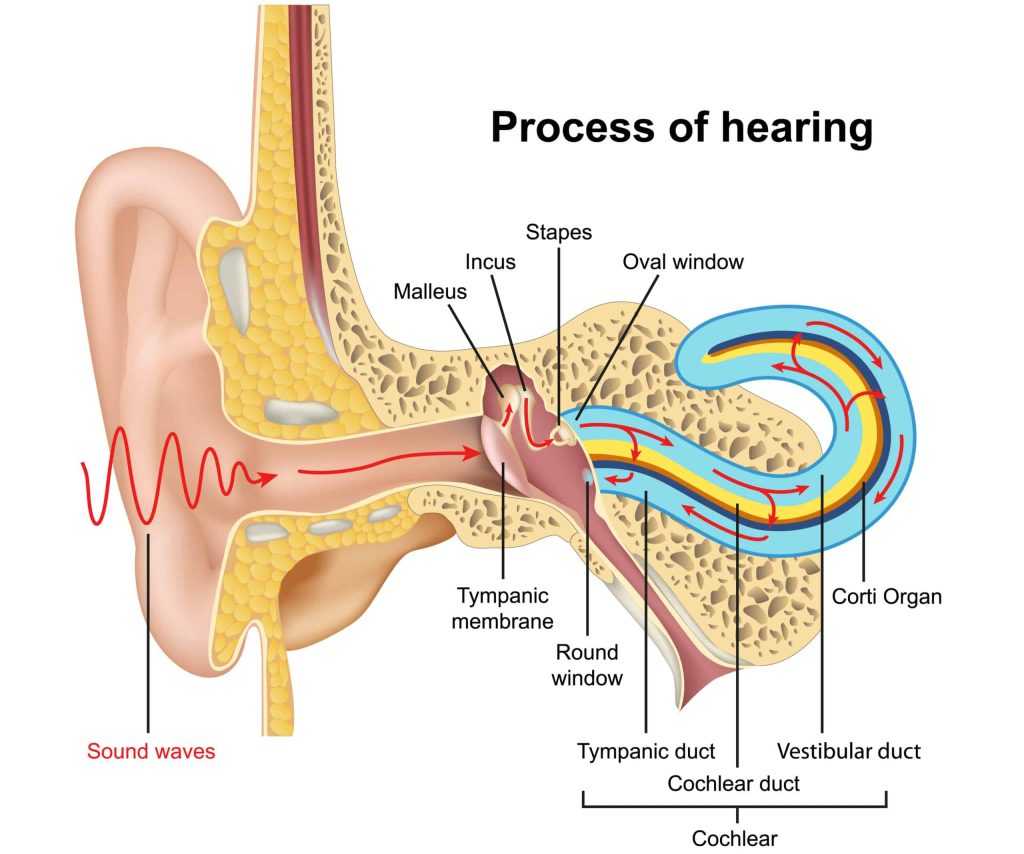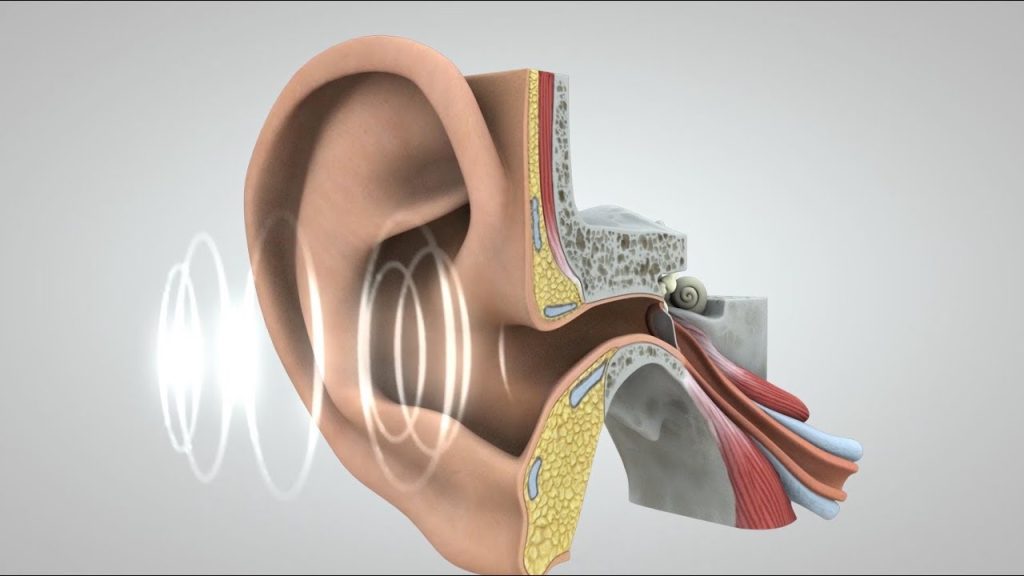
The ear is an organ responsible for hearing and the sense of balance. It contains a number of different components that work together to detect sound and convert it into electrical signals that are sent to the brain. The outer ear, or pinna, collects sound waves and directs them into the ear canal. The ear canal funnels the sound waves to the eardrum, which vibrates in response. The vibrations are then passed through a series of tiny bones in the middle ear called the ossicles. The ossicles amplify the sound waves and send them through the oval window into the inner ear. The inner ear is filled with fluid and contains the cochlea, a spiral-shaped organ lined with thousands of tiny hair cells. These hair cells detect the sound waves and convert them into electrical signals, which are then sent to the brain via the auditory nerve.