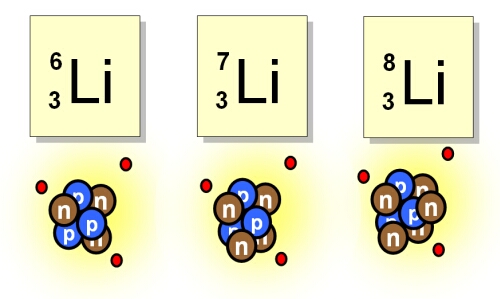
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. They have the same number of protons, and thus the same atomic number, but different atomic masses. Examples of isotopes include carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14.
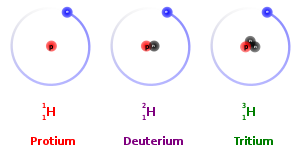
Protium, deuterium, and tritium are three of the most common isotopes of hydrogen. Protium has no neutrons, deuterium has one neutron, and tritium has two neutrons.