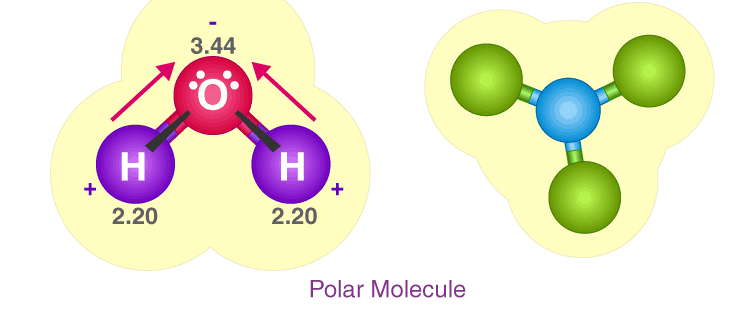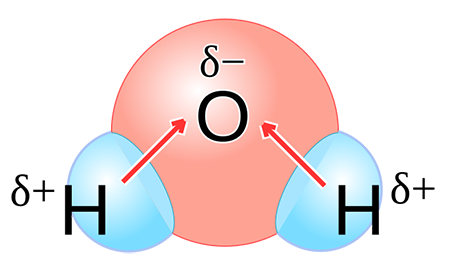
Polarity, in chemistry, is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an overall negative or positive charge. Examples of molecules exhibiting polarity include water, ammonia, and hydrogen chloride. Polar molecules interact through dipole–dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds.