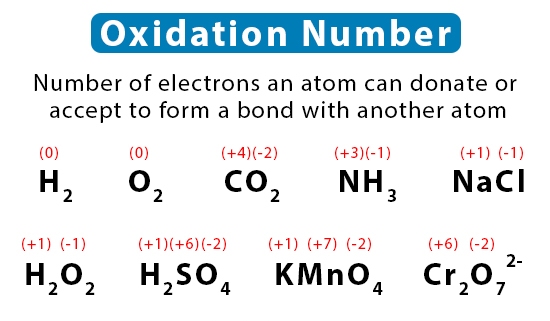
Oxidation number is a number assigned to an atom in a molecule which represents the degree of oxidation of that atom. Oxidation numbers are typically written as a superscript to the right of the symbol for the element. The following are examples of oxidation numbers:
- Oxygen in its elemental form has an oxidation number of 0.
- Hydrogen in its elemental form has an oxidation number of +1.
- Fluorine in its elemental form has an oxidation number of -1.
- Sodium in its elemental form has an oxidation number of +1.
- Chlorine in its elemental form has an oxidation number of -1.
- In the compound NaCl (sodium chloride), the oxidation number of sodium is +1 and the oxidation number of chlorine is -1.
- In the compound H2O (water), the oxidation number of hydrogen is +1 and the oxidation number of oxygen is -2.
- In the compound HClO4 (perchloric acid), the oxidation number of hydrogen is +1, the oxidation number of chlorine is +7, and the oxidation number of oxygen is -2.
