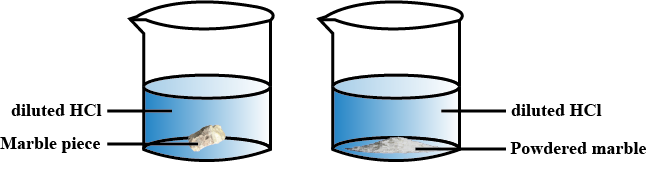
Surface area of a solid is a measure of the total area of its exposed surface. The amount of surface area affects the rate of a chemical reaction because the larger the surface area, the more molecules that are exposed, which increases the reaction rate. For example, if you have a solid cube and you divide it into smaller cubes, each with a smaller surface area, the reaction rate will be slower than if the cube was kept as one large cube with a larger surface area.
