Salts
Salts are ionic compounds that are made up of cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negatively charged ions). Common salts are sodium chloride, potassium chloride, magnesium chloride, and calcium chloride. Salts are used as preservatives, flavour enhancers, and in a variety of other food applications. They are also used for water softening and for cleaning. When salts are dissolved in water, they undergo a number of chemical reactions, including neutralization, precipitation, and exchange reactions. In neutralization reactions, the cations and anions of the salt react with each other to form a neutral salt solution. In precipitation reactions, ions from the salt react with other ions in the solution to form an insoluble solid. Exchange reactions occur when two ions from different salts exchange places in the solution.
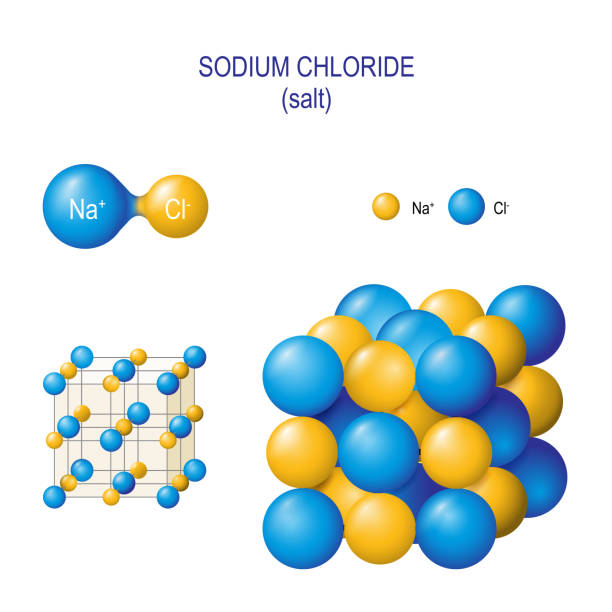
The methods of writing chemical formulae of salt

The chemical formula of a salt is written by using the symbols of its constituent elements, followed by the numerical ratio of the atoms in the compound. For example, the formula for sodium chloride is written as NaCl, indicating that there is one atom of sodium (Na) for every atom of chlorine (Cl) in the compound.
The other way to write the chemical formula of a salt is to use its systematic name. A systematic name is an internationally accepted name that identifies the compound based on its chemical structure. For example, the systematic name of sodium chloride is sodium chloride, which can also be written as NaCl.
