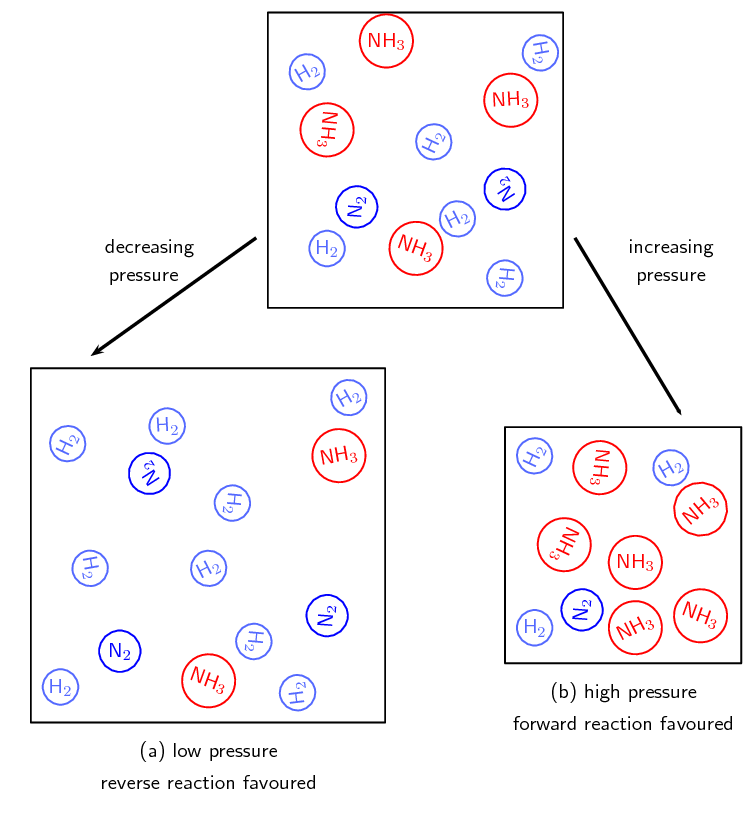
Pressure is a measure of the force exerted on a given area, and is typically expressed in units of atmospheres (atm). Chemical equilibrium is a state in which the concentrations of reactants and products in a chemical reaction remain constant over time. This means that the forward and reverse reactions are occurring at the same rate. When a system is in equilibrium, the pressure of the system is also constant. This is because changes in pressure can affect the equilibrium concentrations of reactants and products, leading to a shift in the equilibrium position.
