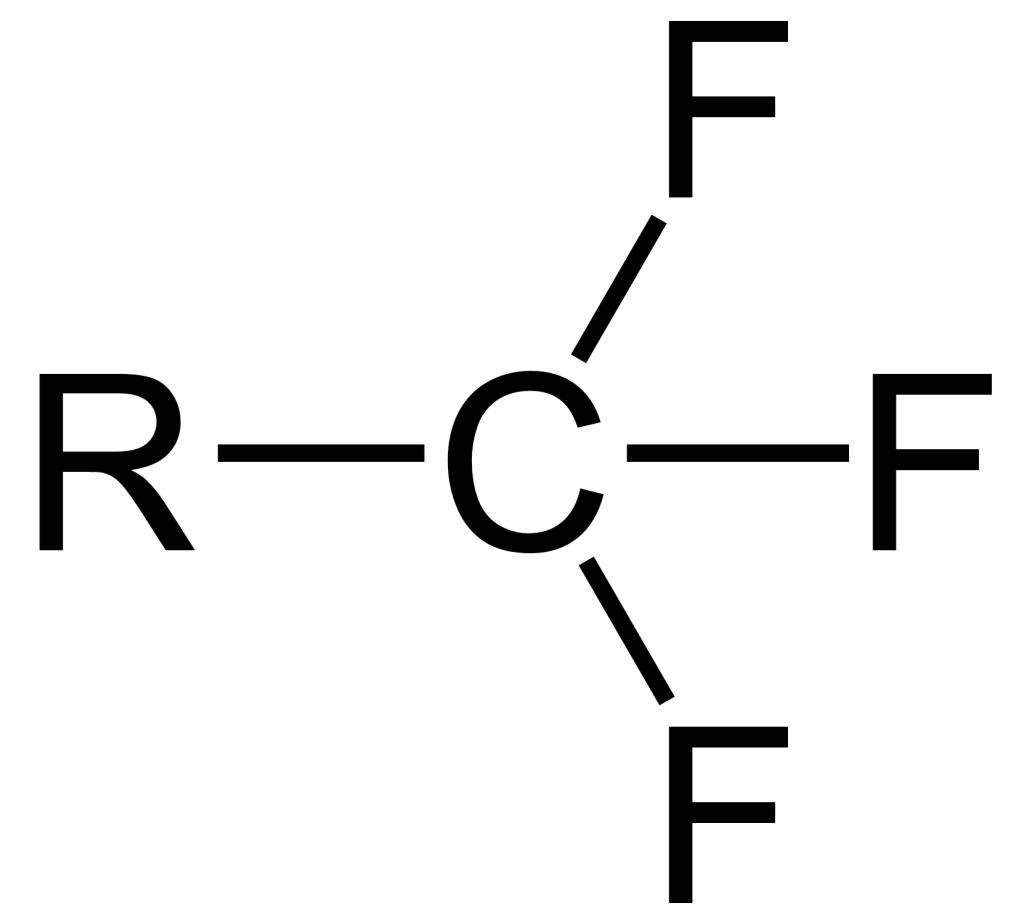
In organic chemistry, a halo group is a functional group consisting of one or more halogens (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine) attached to an aromatic or aliphatic carbon atom. For example, CF3, or trifluoromethyl group, is a halo group. Halo groups are classified as alkyl or aryl depending on the type of carbon to which they are attached.
