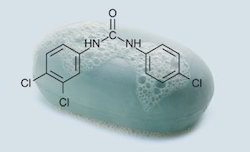
Soap is a salt of a fatty acid that is used in conjunction with water for washing and cleaning. It is usually made from lye and vegetable or animal fat. Soap has many applications in chemistry, including as a surfactant, for its ability to reduce the surface tension of water. It is also used in laboratory testing, as a reagent for precipitation, and for its ability to bind to and remove certain compounds
