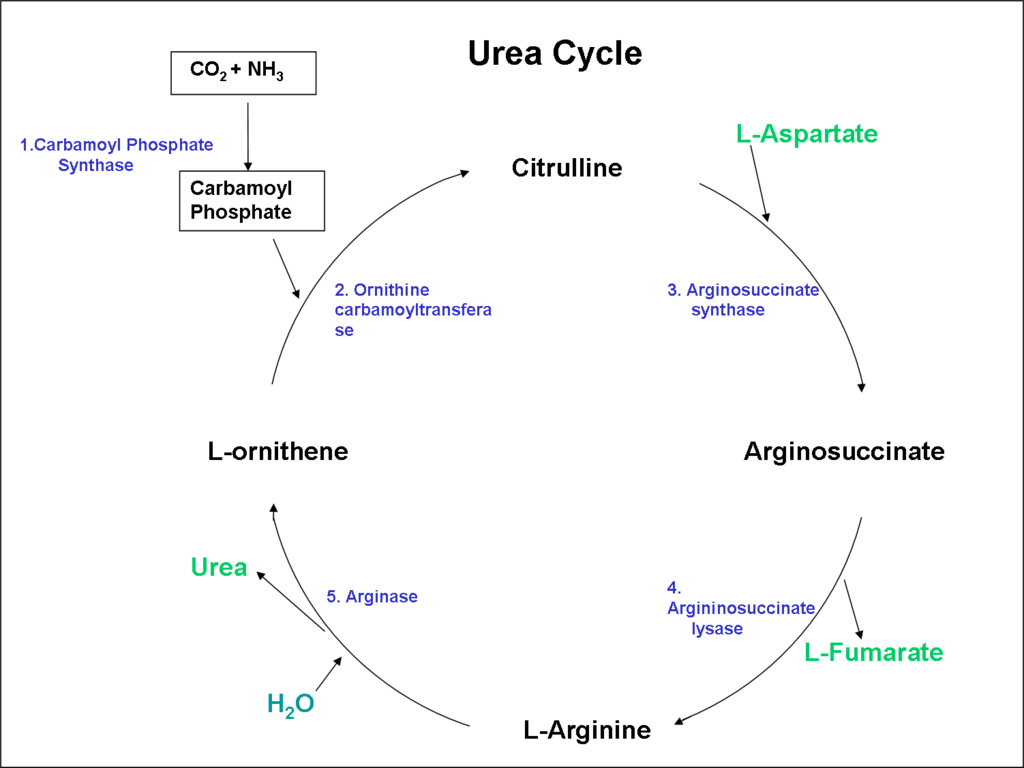
Urea synthesis is a process by which ammonia and carbon dioxide react to form urea. The reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme urease, and occurs in two steps.
In the first step, ammonia and carbon dioxide react to form ammonium carbamate. This reaction is reversible, meaning the product can revert back to its reactants, and is favored at a low pH.
In the second step, ammonium carbamate is hydrolyzed to form urea and water. This reaction is irreversible and is favored at a higher pH.
Overall, the reaction of ammonia and carbon dioxide can be written as follows:
NH3 + CO2 → NH2COONH4 → CO(NH2)2 + H2O
