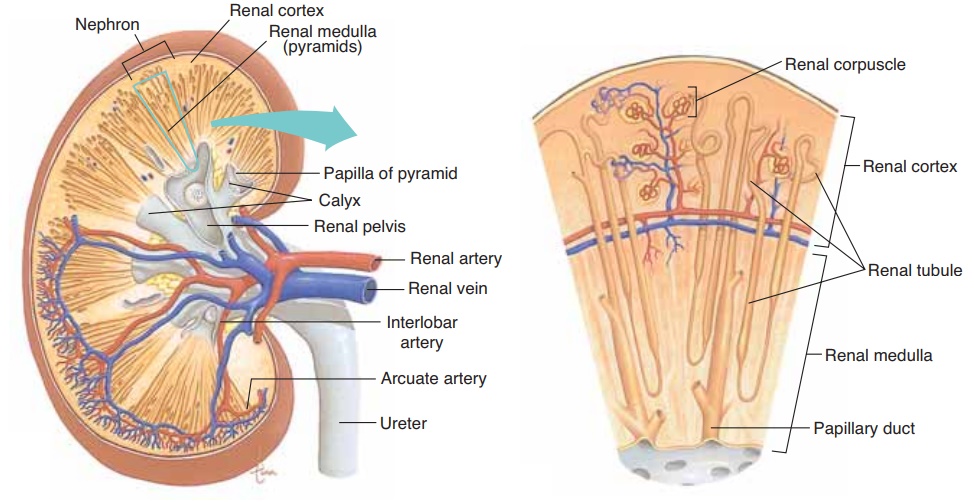
The kidney is composed of an outer cortex and an inner medulla. The medulla is divided into 8 to 18 cone-shaped sections known as renal pyramids. The cortex and medulla are connected by a thin band of tissue known as the renal column. The nephrons are the functional units of the kidney and are responsible for filtering the blood. Each nephron is composed of a glomerulus, Bowman’s capsule, proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule, and collecting duct. The glomerulus is a cluster of capillaries surrounded by Bowman’s capsule. The proximal and distal convoluted tubules are involved in reabsorption of important substances into the blood. The loop of Henle is a U-shaped structure involved in the production of concentrated urine. The collecting ducts are the final destination of the filtrate, where it is either reabsorbed or excreted as urine. The nephrons are arranged in radial columns in the cortex around the renal pyramids.
