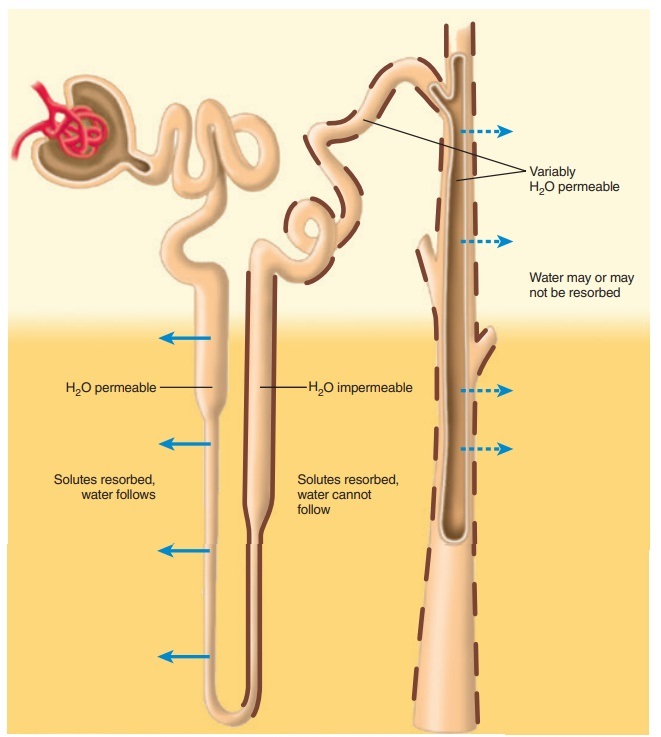
Reabsorption is a process by which the body reclaims certain molecules from the filtrate in the kidneys. It occurs mainly in the proximal tubules of the nephrons of the kidneys, and involves the active transport of molecules from the filtrate back into the bloodstream. The components of reabsorption are sodium, chloride, and glucose, as well as other ions and molecules.
Secretion is a process by which the body eliminates certain molecules from the bloodstream. It occurs mainly in the distal tubules of the nephrons of the kidneys, and involves the active transport of molecules from the bloodstream into the filtrate. The components of secretion are potassium, hydrogen, ammonia, and urea, as well as other ions and molecules.
