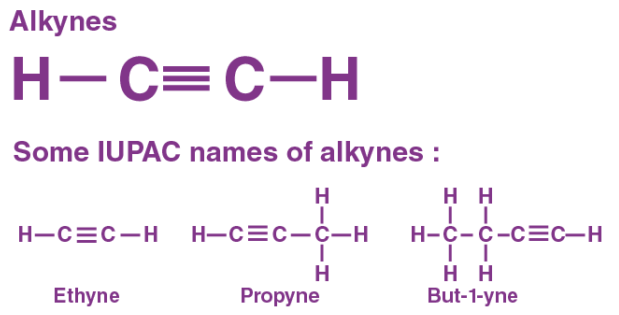
An alkyne is an organic molecule containing a carbon-carbon triple bond. Alkynes are characterized by the general chemical formula CnH2n-2, where n is the number of carbon atoms in the molecule. Alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbons, as they contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond or triple bond. Examples of alkynes include ethyne (C2H2), propyne (C3H4), and phenylacetylene (C6H5CCH).
