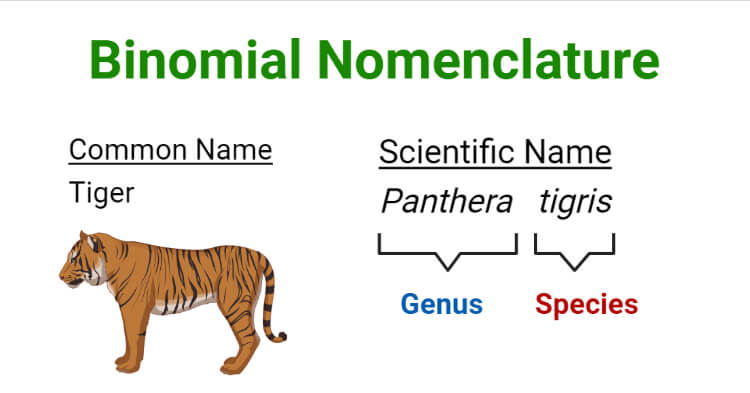
Binomial nomenclature is a system of naming species of living things by giving each species a name composed of two parts. The first part of the name identifies the genus to which the species belongs, while the second part identifies the species within the genus. For example, the scientific name of humans is Homo sapiens. Here, Homo is the genus and sapiens is the species within the genus Homo. The binomial system of nomenclature was developed by Carl Linnaeus, a Swedish botanist, zoologist, and physician, in the 18th century. He is regarded as the father of modern taxonomy. The binomial system is internationally accepted and is used by scientists all around the world.
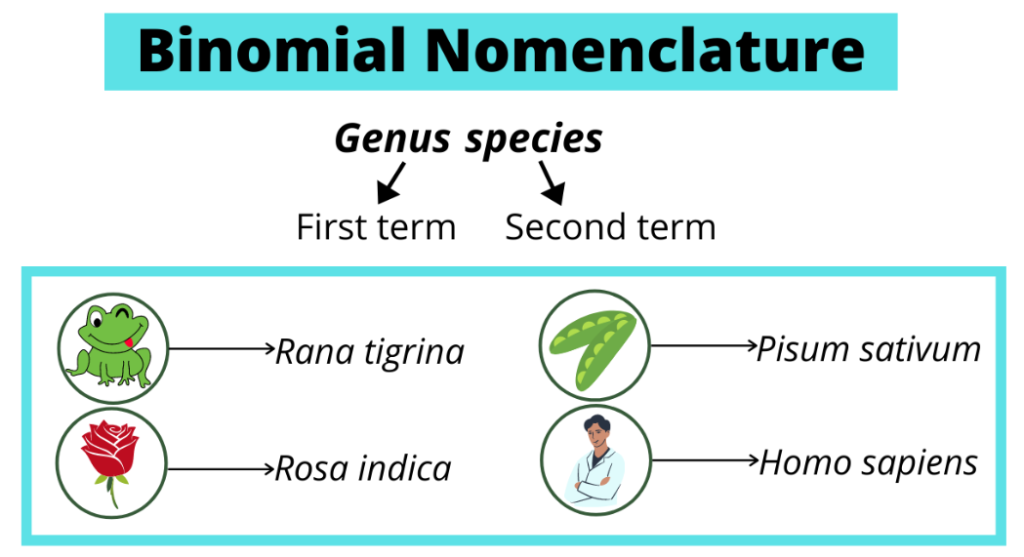
Binomial nomenclature,
Carl Linnaeus ,
father of modern taxonomy
