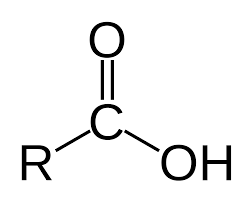
Carboxylic acids are organic acids that contain a carboxyl group (-COOH) attached to an alkyl group. The general formula for carboxylic acids is R-COOH, where R is an alkyl group. Carboxylic acids are classified as either weak acids or strong acids depending on their acidity. Weak acids are generally more soluble in water than strong acids. Weak carboxylic acids generally have lower pKa values than strong carboxylic acids. Examples of weak carboxylic acids include acetic acid (pKa 4.76), propionic acid (pKa 4.88), and lactic acid (pKa 3.86). Examples of strong carboxylic acids include formic acid (pKa 3.75) and oxalic acid (pKa 1.25). Carboxylic acids can react with other compounds to form esters, amides, and other derivatives.
