Skip to content
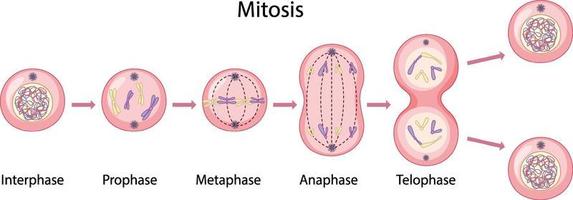
- Mitosis is the process of eukaryotic cell division where the cell nucleus splits into two identical daughter nuclei.
- It is followed by the division of the cytoplasm and the organelles, resulting in two daughter cells.
- Mitosis is a continuous process, which is divided into four stages: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- During prophase, the chromosomes condense and become visible.
- During prometaphase, the nuclear envelope breaks down and the spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes.
- During metaphase, the chromosomes align themselves in the middle of the cell.
- During anaphase, the chromosomes are pulled apart and move to opposite ends of the cell.
- During telophase, the two sets of chromosomes arrive at opposite ends of the cell and a new nuclear envelope forms around each set.
- Finally, cytoplasm is divided equally between the two daughter cells.