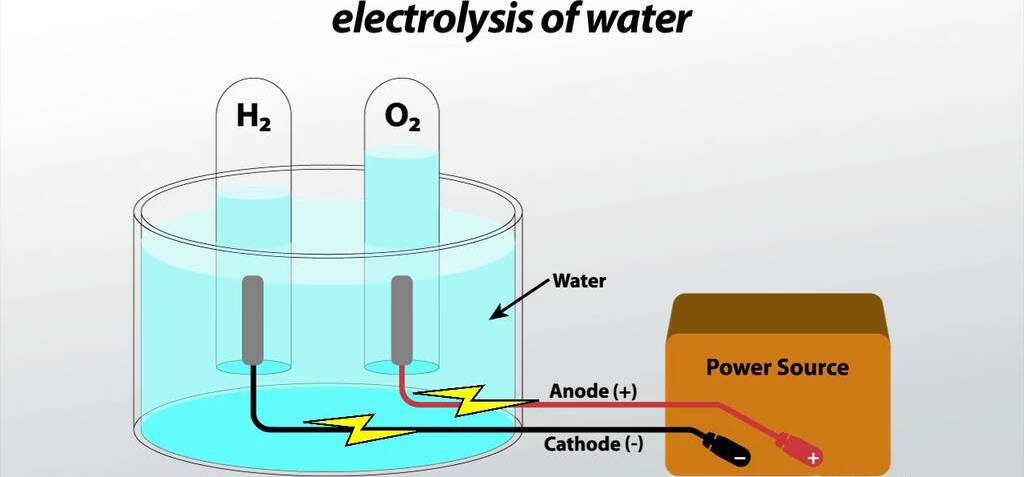
- Prepare a solution of water and acid by mixing equal parts of the two together in a beaker. The acid used should be strong enough to provide a good electrical conductivity.
- Connect the electrodes (anode and cathode) to a DC power source, and immerse them in the solution. Make sure the anode is connected to the positive terminal and the cathode is connected to the negative terminal of the power source.
- Turn on the power source, and wait until bubbles of hydrogen gas (H2) appear at the anode, and oxygen gas (O2) appears at the cathode. This indicates that the electrolysis reaction has begun.
- Monitor the progress of the reaction. When the reaction is finished, turn off the power source and disconnect the electrodes.
- Observe the solution, and note the presence of the hydrogen gas (H2) and oxygen gas (O2).
- Dispose of the solution according to your local regulations.
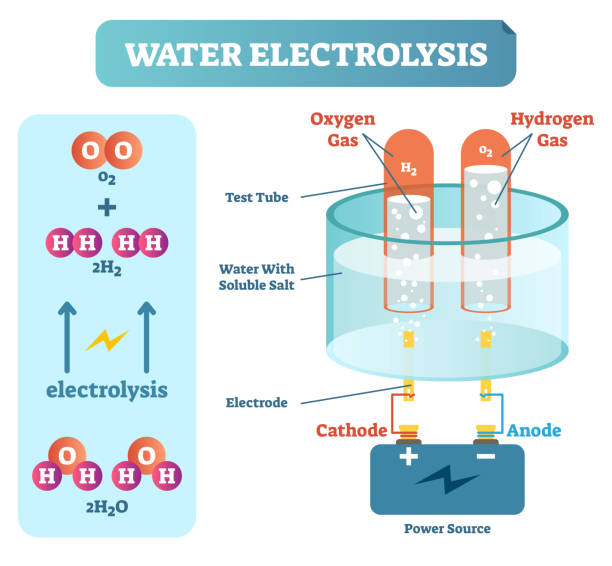
The components of water are hydrogen and oxygen. In this experiment, acid is added to water to create hydrogen ions (H+), and electricity is passed through the water to create hydroxide ions (OH-). When these two ions combine, they form water (H2O) and release hydrogen gas (H2). This experiment demonstrates the process of electrolysis, which is the breakdown of water into its component elements using electricity. The acid helps to increase the conductivity of the solution, allowing the electricity to pass more easily through the water and cause the electrolysis reaction.
