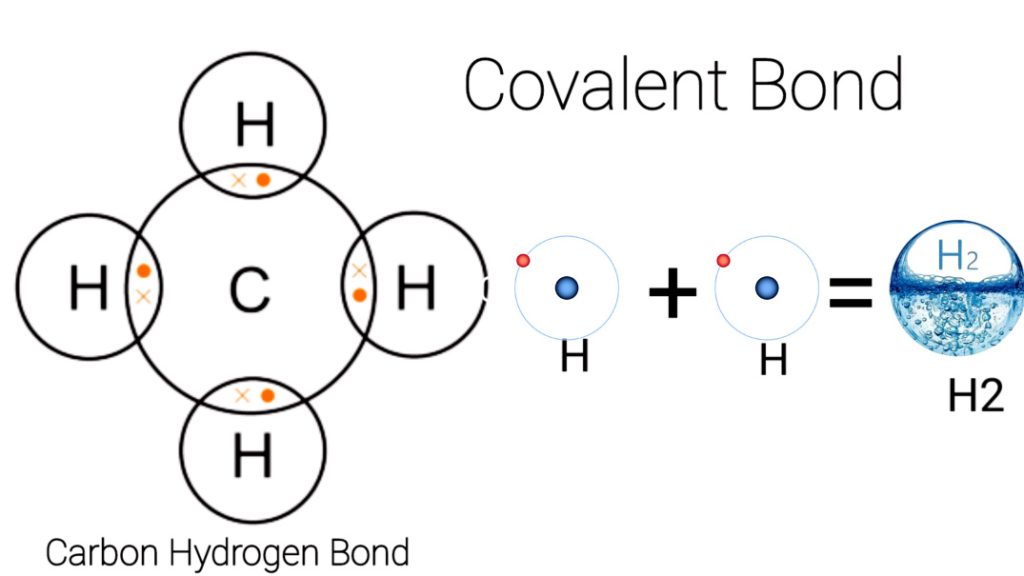
Covalent bonding is a type of chemical bonding that involves the sharing of one or more pairs of electrons between two or more atoms. Examples of covalent bonding include water, carbon dioxide, methane, and ammonia. Water is formed when two hydrogen atoms covalently bond with an oxygen atom. Carbon dioxide is formed when one carbon atom covalently bonds with two oxygen atoms. Methane is formed when four hydrogen atoms covalently bond with one carbon atom. Ammonia is formed when three hydrogen atoms covalently bond with one nitrogen atom.
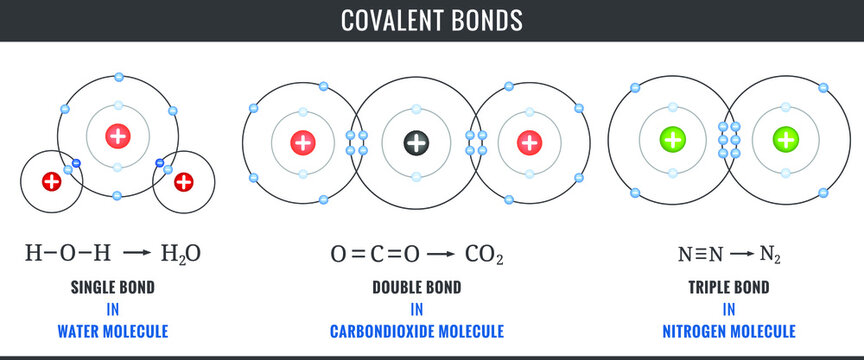
- Water molecules (H2O)
- Table salt (NaCl)
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Methane (CH4)
- Ethanol (C2H6O)
- Diamond (C)
- Ammonia (NH3)
- Hydrogen sulphide (H2S)
- Glucose (C6H12O6)
- Silicon dioxide (SiO2)
Covalent compounds
Covalent compounds are chemical compounds in which atoms are held together by covalent bonds. These bonds form when atoms of different elements share electrons in order to form a stable bond. Examples of covalent compounds include water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and ammonia (NH3).
