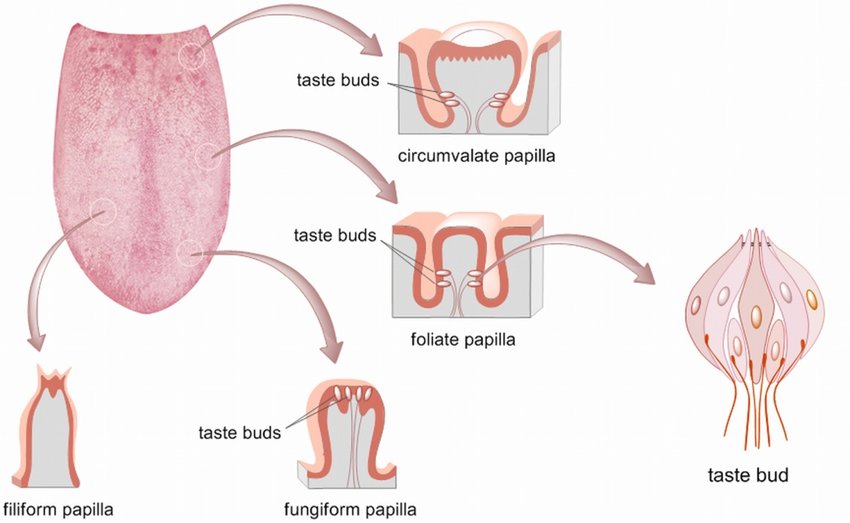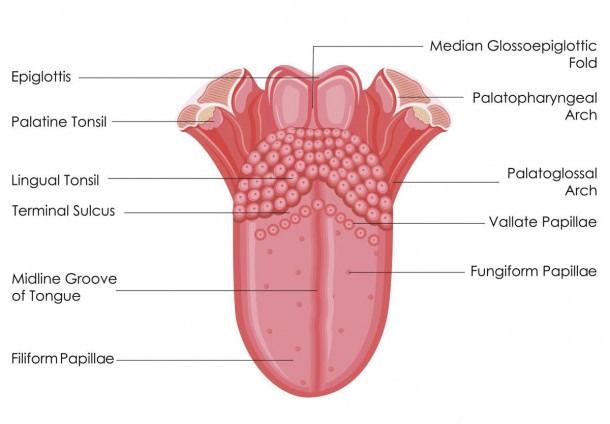
Chemoreceptors are sensory receptors that detect chemical changes in the environment and trigger a response in the body. Examples of chemoreceptors include taste buds, which detect the presence of sugars and other compounds in food, and olfactory receptors, which detect odours .Taste buds are sensory organs on the tongue that contain taste receptor cells, which allow us to detect the five basic tastes: sweet, salty, sour, bitter, and umami.Papillae are small, raised bumps found on the surface of the skin, tongue, or other body parts. They are often present in groups, forming linear or circular patterns. Papillae contain nerve endings and are responsible for sensations such as touch and taste. In the tongue, papillae help to detect different flavours in food.
Chemoreceptors help to detect and respond to chemicals in the environment. They are found in the nose and on the tongue, and they help to detect tastes and smells.