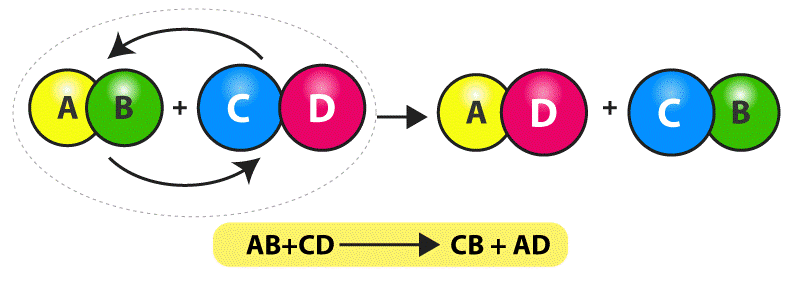
Double decomposition is a type of chemical reaction in which two reactants exchange ions to form two new products. It is also known as a double displacement reaction or a metathesis reaction. The general equation for a double decomposition reaction is: A + B → C + D. In this equation, A and B are two reactants that exchange ions and form two new products, C and D. Double decomposition reactions can be used to precipitate a solid from a solution, form an emulsion, or neutralize an acid or a base.
One example of a double decomposition reaction is the reaction between silver nitrate (AgNO3) and potassium chloride (KCl):
AgNO3 + KCl → AgCl + KNO3
In this reaction, the silver nitrate and potassium chloride exchange a nitrate ion and a chloride ion, forming two new products, silver chloride (AgCl) and potassium nitrate (KNO3). Silver chloride is a white precipitate, which is a solid that forms in a reaction and is visible in the reaction mixture.
Identification of chlorides
