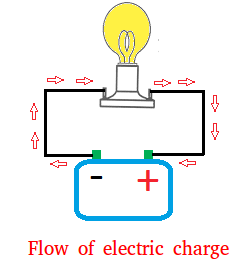
Electric charge flows through an electrical circuit when a potential difference, or voltage, is applied across the circuit. The flow of electric charge is called an electric current, and it is measured in units called amperes. In a circuit, electric charge flows from the negative terminal of the voltage source (such as a battery) to the positive terminal, passing through all the components of the circuit as it goes.
