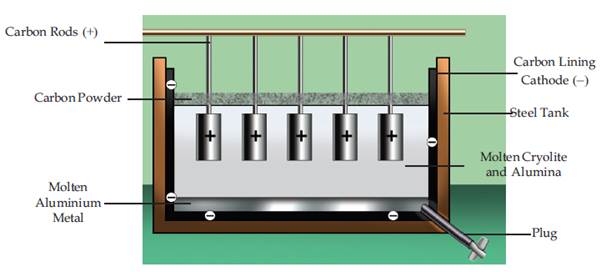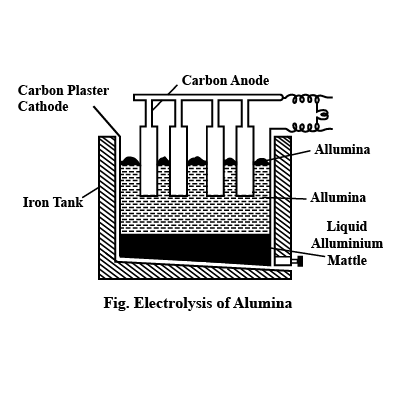
Alumina (Al2O3) is a compound of aluminium and oxygen. It is insoluble in water and does not react with acids or bases. However, it can be broken down into its component ions by electrolysis. In the electrolysis of alumina, the solid is dissolved in a molten solution of cryolite (Na3AlF6) and the ions are separated using electricity. The positive ions (Al3+) move to the anode, where they are reduced to metallic aluminium. The negative ions (O2-) move to the cathode where they are oxidized to form oxygen gas. The molten electrolyte is continuously replenished with alumina and cryolite to replace the aluminium and oxygen that are removed. The aluminium produced is of a high purity and can be used in the production of many products.
Al2O3 + 6 H2O → 4 Al (OH)3 + 3 O2