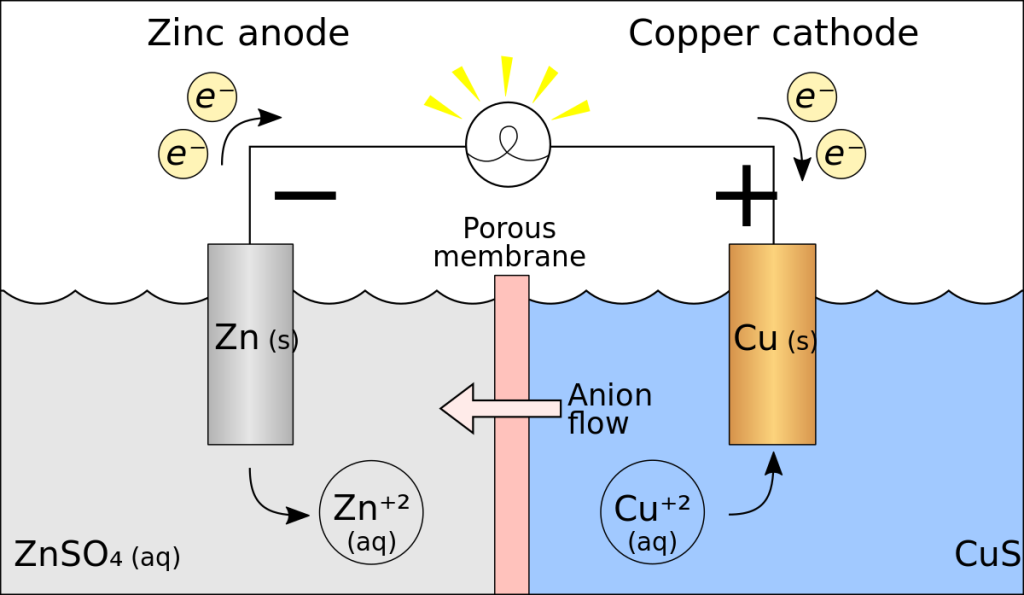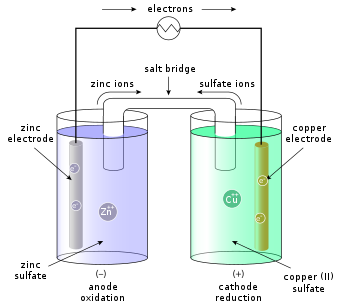
A galvanic cell, also known as a voltaic cell, is an electrochemical cell that produces electricity from a chemical reaction. The reaction involves the transfer of electrons from a metal electrode to an electrolyte, which is usually an aqueous solution of an acid or a base. The electricity produced is used to power electrical devices, such as lights, motors, and computers. Galvanic cells are the basis of most batteries, including the lead-acid battery and lithium-ion battery.
The reaction between the zinc rod and the copper rod in the zinc sulphate and potassium chloride bridge is a redox reaction. The zinc rod is oxidized, giving up electrons to the bridge, and the copper rod is reduced, taking up electrons from the bridge. At the anode (the zinc rod), the reaction is:
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e-
At the cathode (the copper rod), the reaction is:
Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu
The overall reaction is:
Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu