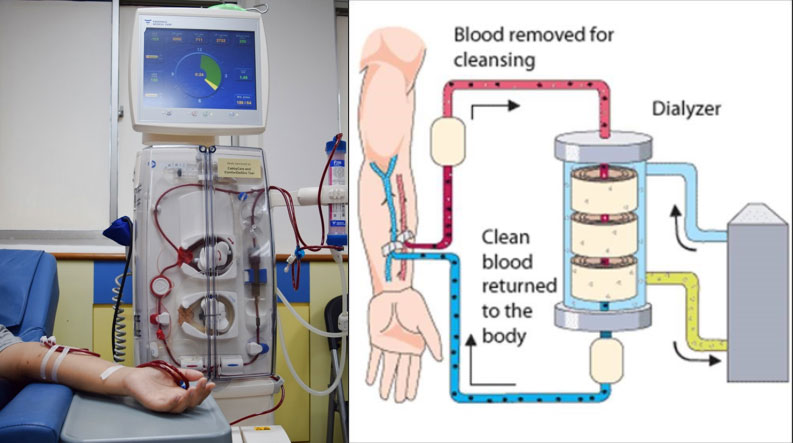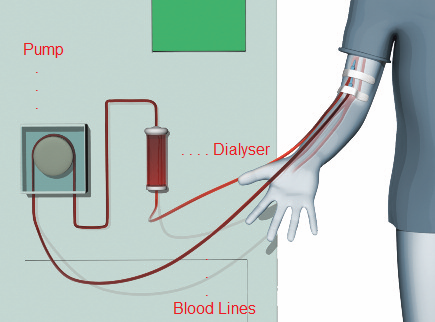
Haemodialysis is a type of dialysis used to remove waste products and excess fluids from the body. It is a medical procedure used to treat patients with kidney failure, also known as end-stage renal disease (ESRD). It is a process where blood is removed from the body and passed through a dialysis machine, which filters out unwanted substances, such as urea and creatinine, and returns the clean blood to the body. The process involves a two-way exchange of substances between the patient’s blood and the dialysate, a solution which contains electrolytes, minerals and other substances needed to keep the body in balance. In haemodialysis, a dialyser is used, which is a membrane that allows for the exchange of substances between the blood and the dialysate. The process of haemodialysis typically takes three to four hours and is usually done three times a week. It is used to treat a variety of conditions, including high blood pressure, fluid retention, and acidosis.