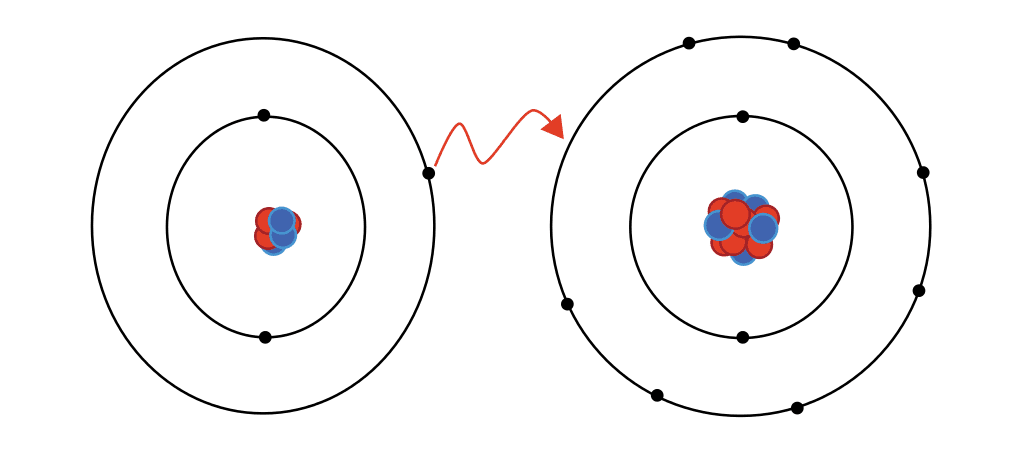
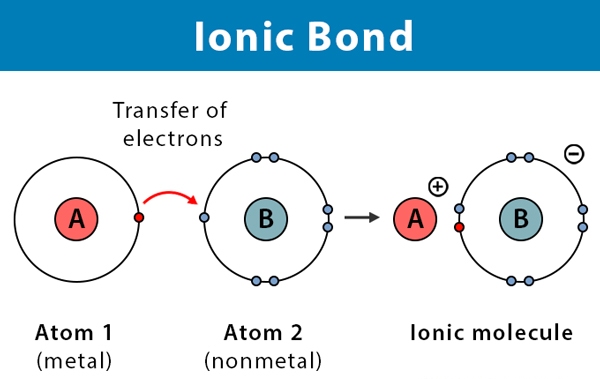
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that involves the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. It is a type of electrostatic interaction between two oppositely charged ions, and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compounds. A classic example of ionic bonding is the combination of sodium (Na+) and chlorine (Cl−) to form sodium chloride (NaCl). The transfer of an electron from sodium to chlorine results in the formation of an ionic bond, as both ions now have a full valence shell. The electrostatic attraction between the two ions holds them together, forming an ionic compound.
Other examples of ionic bonding include:
- Magnesium oxide (MgO)
- Potassium iodide (KI)
- Calcium carbonate (CaCO3)
- Sodium sulfate (Na2SO4)
- Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl)
- Potassium oxide (K2O)
- Beryllium chloride (BeCl2)
- Lead (II) sulphide (PbS)
