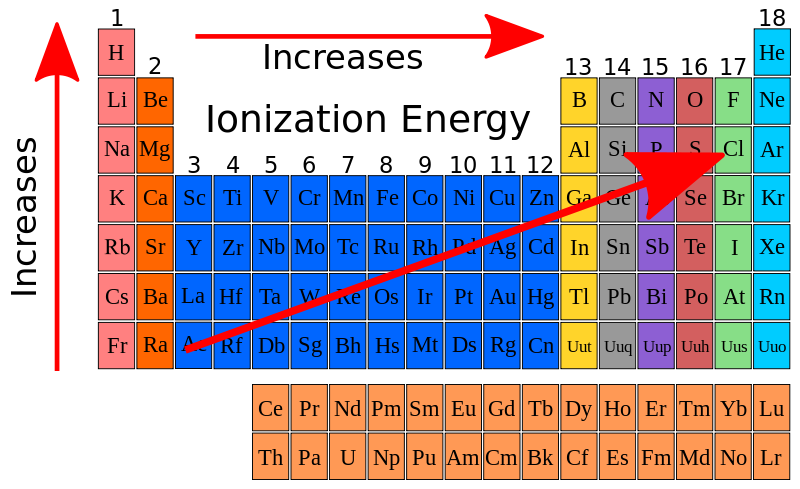
Ionisation energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom or molecule in the gaseous state. It is usually expressed in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol).
For example, the first ionisation energy of hydrogen is 1312 kJ/mol. This means that 1312 kJ of energy is required to remove 1 mole of electrons from 1 mole of hydrogen atoms.
