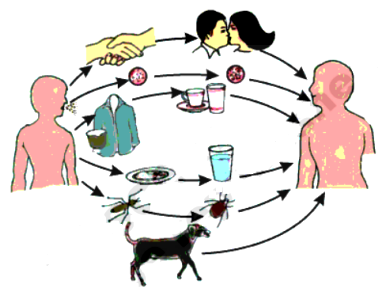
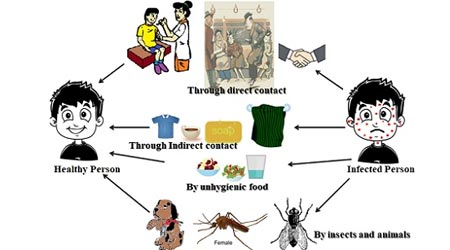
Diseases can be spread through various modes of transmission, including direct and indirect contact, airborne and vector-borne transmission, and through food and water.
- Direct contact: Direct contact involves physical contact between two people, such as through sexual contact, kissing, or touching. This is the most common mode of transmission for many infectious diseases, such as influenza, herpes, and the common cold.
- Indirect contact: Indirect contact involves contact with an infected person’s body fluids, such as blood, saliva, vomit. This is a common mode of transmission for many diseases, such as HIV, hepatitis B and C, and typhoid.
- Airborne transmission: Airborne transmission occurs when an infected person coughs or sneezes, releasing small particles into the air that can be inhaled by another person. This is a common mode of transmission for diseases such as the flu, measles, and tuberculosis.
- Vector-borne transmission: Vector-borne transmission occurs when an infected animal, such as a mosquito, tick, or flea, carries and transmits a disease-causing organism to another person. This is the most common mode of transmission for diseases such as malaria, Lyme disease, and dengue fever.
- Food and water: Food and water can be contaminated with bacteria, viruses, or parasites, which can cause food borne illnesses such as salmonellosis and cholera
dicices,diceces
