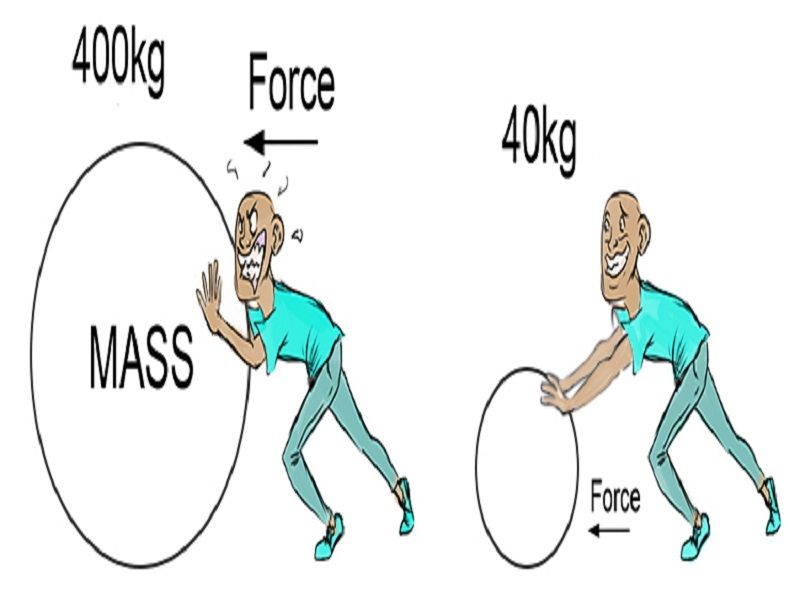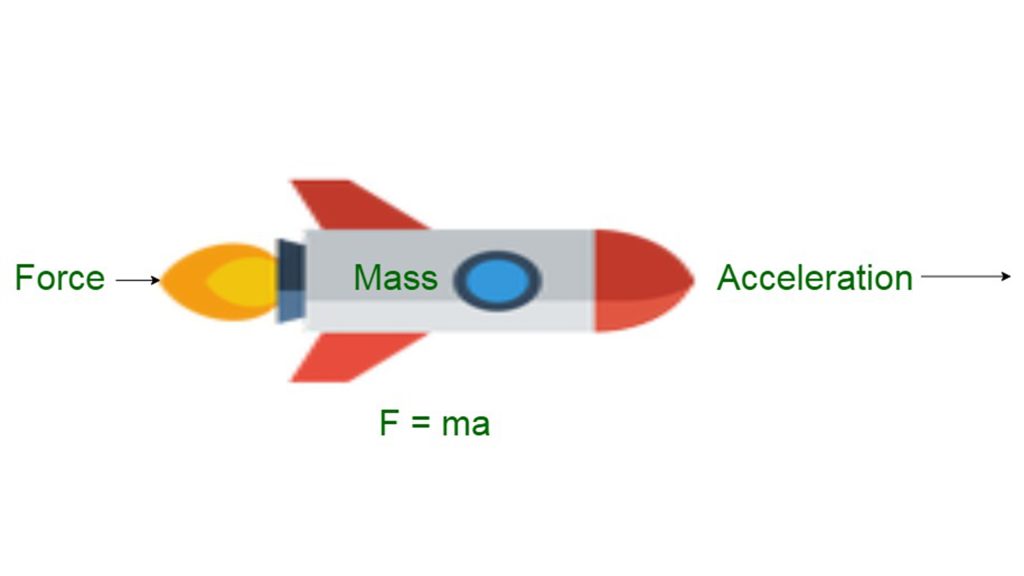
Newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force applied and inversely proportional to its mass. The equation is F = ma, where ‘F’ is the net force, ‘m’ is the mass of the object, and ‘a’ is the acceleration of the object.