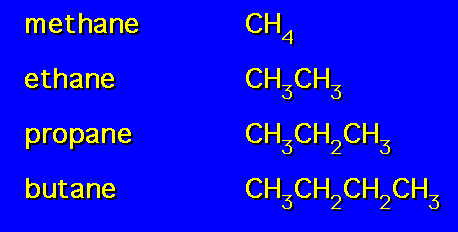
Un branched alkanes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of only single bonds and form a straight chain. The simplest such alkane is methane (CH4). The nomenclature for unbranched alkanes is based on a prefix that denotes the number of carbon atoms in the molecule followed by the suffix -ane. Examples of nomenclature for unbranched alkanes include:
- Methane (CH4): 1-methane
- Ethane (C2H6): 2-ethane
- Propane (C3H8): 3-propane
- Butane (C4H10): 4-butane
- Pentane (C5H12): 5-pentane
- Hexane (C6H14): 6-hexane
- Heptane (C7H16): 7-heptane
- Octane (C8H18): 8-octane
