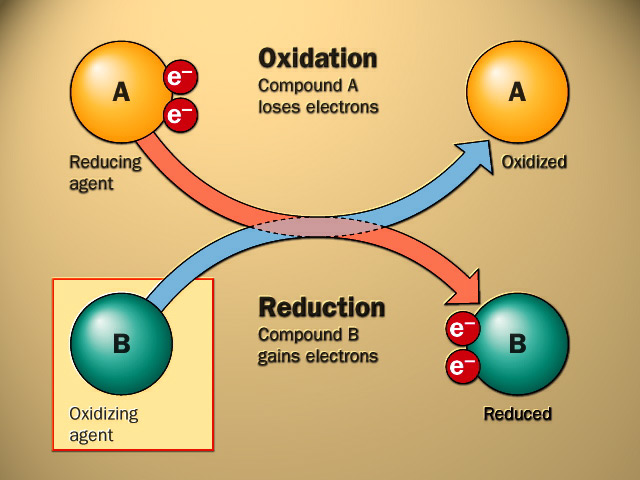
Oxidation: Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Oxidation reactions involve the transfer of electrons from one species to another.
Examples of Oxidation:
- Combustion of ethanol: C2H6O + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O
- Rusting of iron: 4Fe + 3O2 → 2Fe2O3
- Oxidation of Glucose: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
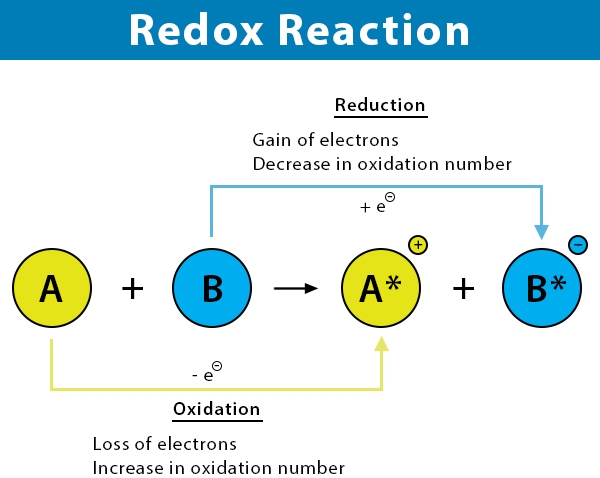
Reduction: Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction reactions involve the transfer of electrons from one species to another.
Examples of Reduction:
- Reduction of Iron Oxide: Fe2O3 + 3H2 → 2Fe + 3H2O
- Reduction of Carbon Dioxide: CO2 + 2H2 → CH3OH
- Reduction of Nitrate: NO3- + 8H+ + 8e- → NH4+
