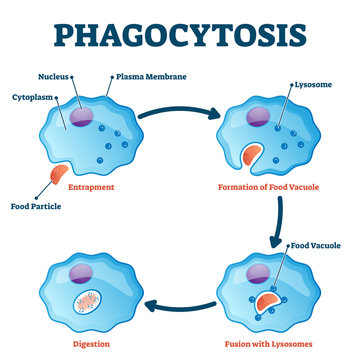
Phagocytosis is a process by which cells, usually white blood cells, engulf and absorb foreign particles, such as bacteria and viruses. This process is part of the innate immune response, which helps defend the body from infection and disease. During phagocytosis, the phagocytes, or white blood cells, first recognize a foreign particle, and then engulf it. They then break down the particle by releasing enzymes and other substances, and finally, the contents of the particle are digested and the cell absorbs the nutrients. Phagocytosis helps protect the body from harmful pathogens and other foreign substances.

fagocytosis, phagositosis
