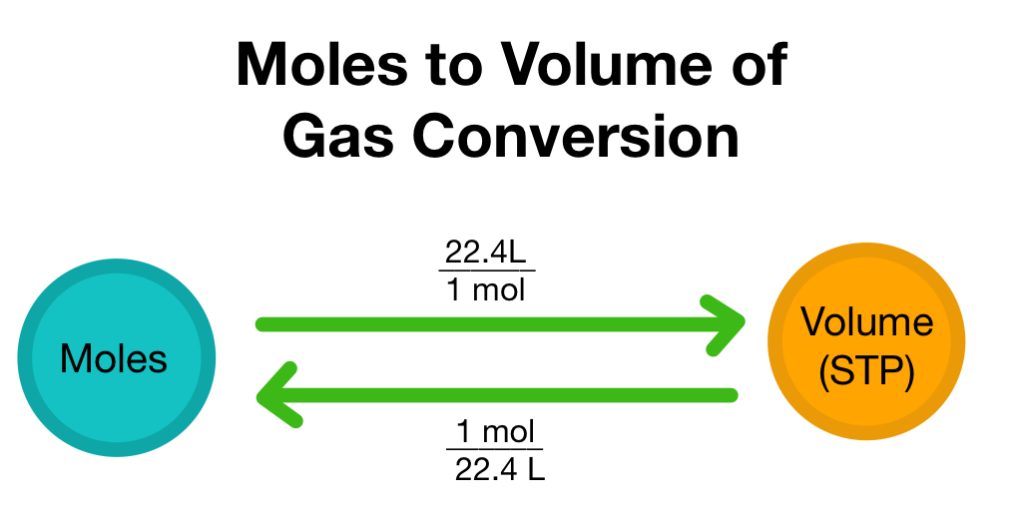
The volume of a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles present. This means that if the number of moles of a gas is increased, the volume of the gas will increase as well. The relationship can be expressed mathematically as: Volume = n × R × T/P, where n is the number of moles of the gas, R is the ideal gas constant, T is the temperature in Kelvin, and P is the pressure.
