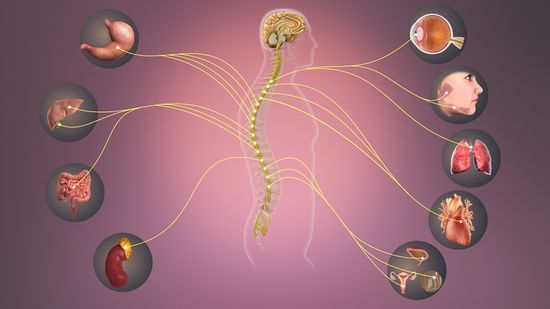
The sympathetic nervous system is part of the autonomic nervous system, which controls and regulates unconscious body functions such as heart rate, digestion, respiration, and internal organ function.
Organs of the sympathetic system include:
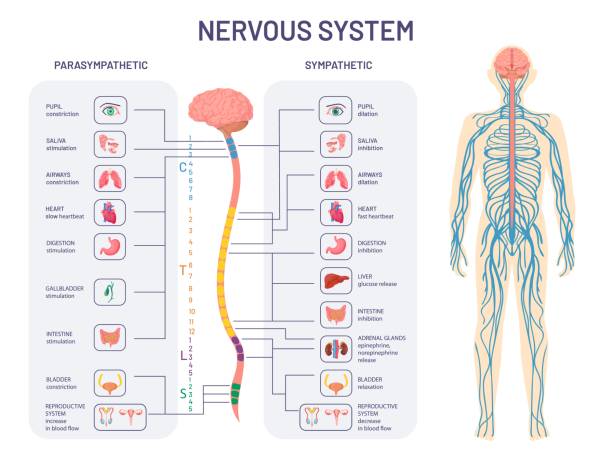
- Adrenal Glands: These are two small glands that sit atop the kidneys and produce hormones, such as adrenaline and cortisol, that regulate a variety of bodily functions.
- Heart: The sympathetic nervous system increases the heart rate, blood pressure, and blood flow in response to stress.
- Lungs: The sympathetic nervous system constricts the airways in the lungs, making it more difficult to breathe during a stressful situation.
- Blood Vessels: The sympathetic nervous system causes the blood vessels to constrict, which helps to increase blood pressure in response to stress.
- Skin: The sympathetic nervous system causes sweat glands to become more active, which helps to cool the body down.
- Eyes: The sympathetic nervous system causes the pupils to dilate, allowing more light to enter the eyes. This helps to improve vision in low-light conditions.
- Digestive System: The sympathetic nervous system slows down the digestive process, which allows the body to focus on more pressing matters.
