Linnaeus’s taxonomic hierarchy, also known as the Linnaean taxonomy, is a system of classification used to organize species into groups. It is one of the most widely used systems of biological classification, and is still in use today.
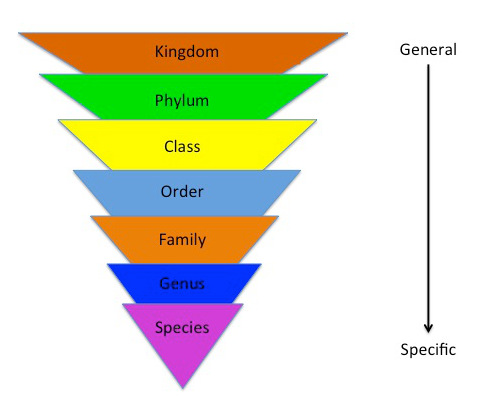
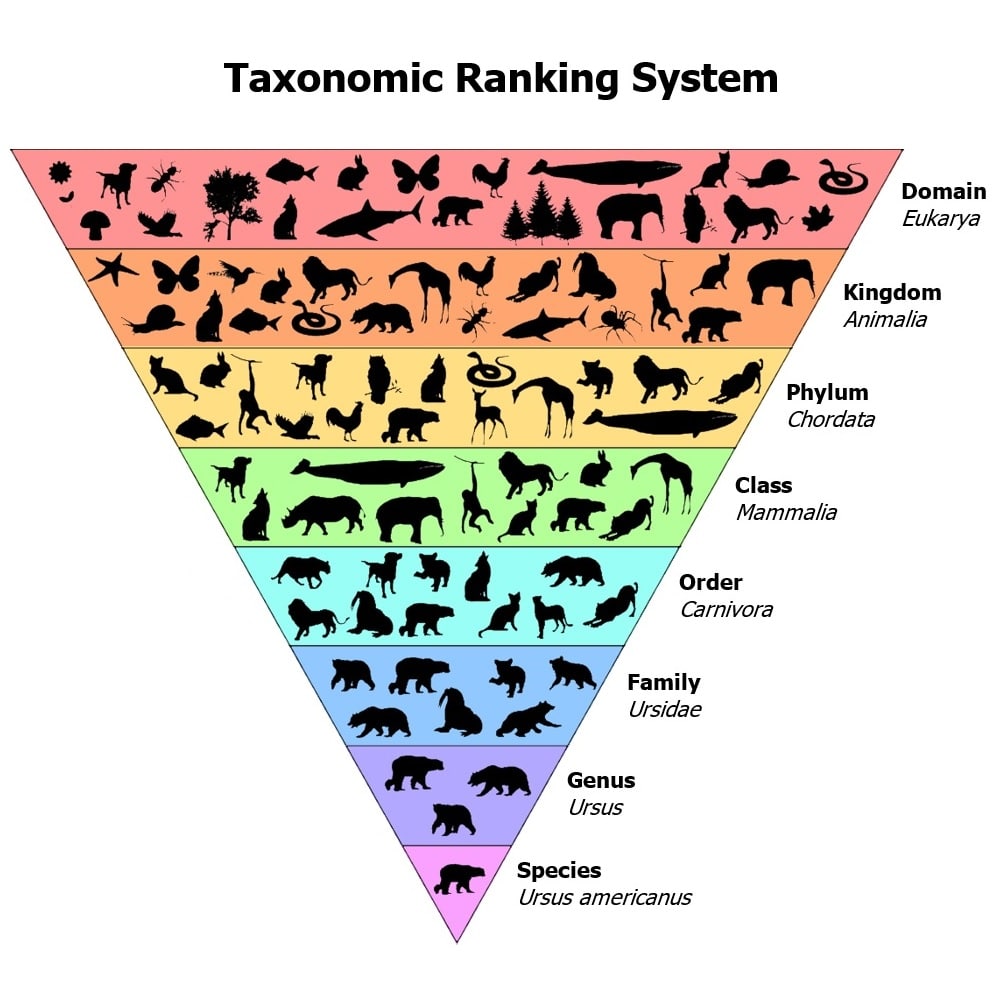
Linnaeus’s taxonomic hierarchy is based on the Aristotelian concept of hierarchical organization, which was further developed by Carl von Linné (Linnaeus). The hierarchy is composed of 7 distinct levels, starting from the most general and working down to the most specific. These levels are:
1. Kingdom
2. Phylum
3. Class
4. Order
5. Family
6. Genus
7. Species
Within each of these levels, organisms are further divided into more specific categories. For example, a species may be divided into subspecies, and a genus may be divided into further genera. This system of classification allows for a more precise description of species and their relationships.
Linnaean taxonomy,
classification,
genera
