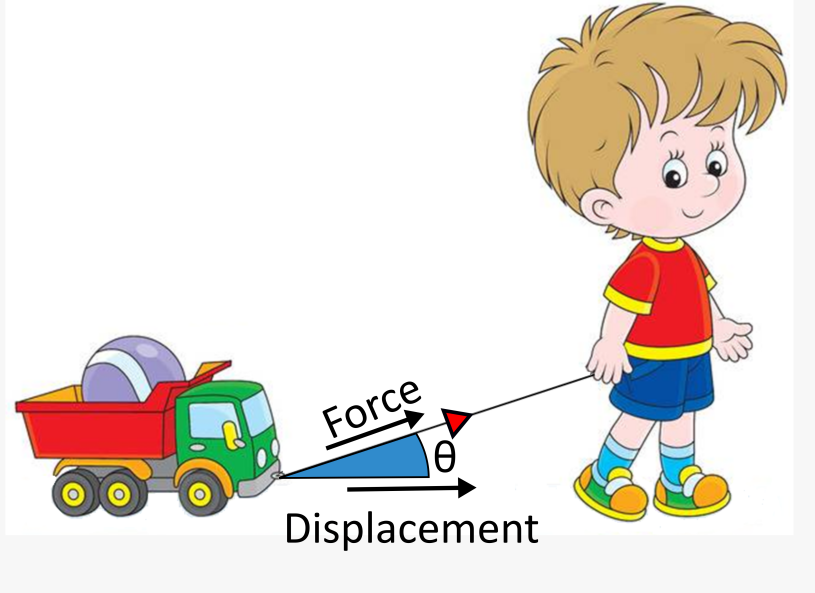
1. Magnitude of the Force: The magnitude of the force applied to complete the work is a key factor. The greater the force, the more work that can be done.
2. Direction of the Force: The direction of the force applied affects the work done. If the force is in the same direction as the movement, more work is done than if it is in the opposite direction.
3. Distance Traveled: The distance traveled by the object on which the force is applied is a factor in determining the work done. The longer the distance, the greater the work done.
4. Duration of the Force: The duration of the force applied is also important. The longer the force is applied, the more work is done.
5. Type of Force: The type of force applied affects the work done. For example, frictional forces can cause an object to slow down, while gravitational forces can cause an object to speed up.
