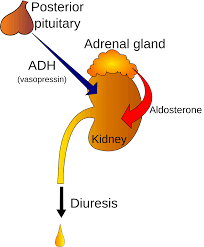
Vasopressin, also known as anti diuretic hormone (ADH), is a hormone released by the posterior pituitary gland, and it plays a major role in the regulation of kidney function. In the kidneys, vasopressin stimulates the re absorption of water into the bloodstream, allowing the body to conserve and conserve water, thus increasing blood volume and blood pressure. Vasopressin also causes the release of renin, an enzyme that helps regulate blood pressure, and it is essential for the proper regulation of electrolyte balance in the body.
The main role of vasopressin in the kidneys is to regulate the water balance of the body. When the body is dehydrated, vasopressin is released, which increases water re absorption in the kidneys, resulting in the retention of water and a decrease in urine production. This helps to prevent dehydration and maintain normal blood pressure.
Vasopressin also plays an important role in the regulation of electrolyte balance in the body. It increases the re absorption of sodium and chloride ions in the kidneys, which helps to maintain the proper balance of these ions in the body.
In addition, vasopressin also helps to regulate blood pressure. By increasing the re absorption of water and electrolytes, it helps to increase blood volume and thus, blood pressure. This helps to maintain a healthy blood pressure, which is important for overall health and well-being.
Overall, vasopressin is essential for the proper regulation of kidney function, as it helps to regulate water balance, electrolyte balance, and blood pressure, all of which are essential for good health.
vasopresin, kignies
