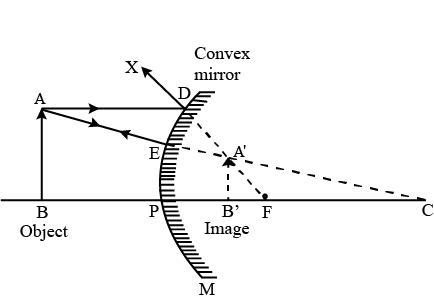
The reason for this is because the light rays from an object are reflected from the surface of the convex mirror in such a way that the reflected rays appear to diverge from a point behind the mirror. Because the light rays never actually meet at this point, the image formed is virtual (meaning that it does not exist on the mirror’s surface). Moreover, the image is erect (meaning that it is upright relative to the object) and diminished (meaning that it is smaller than the object).
