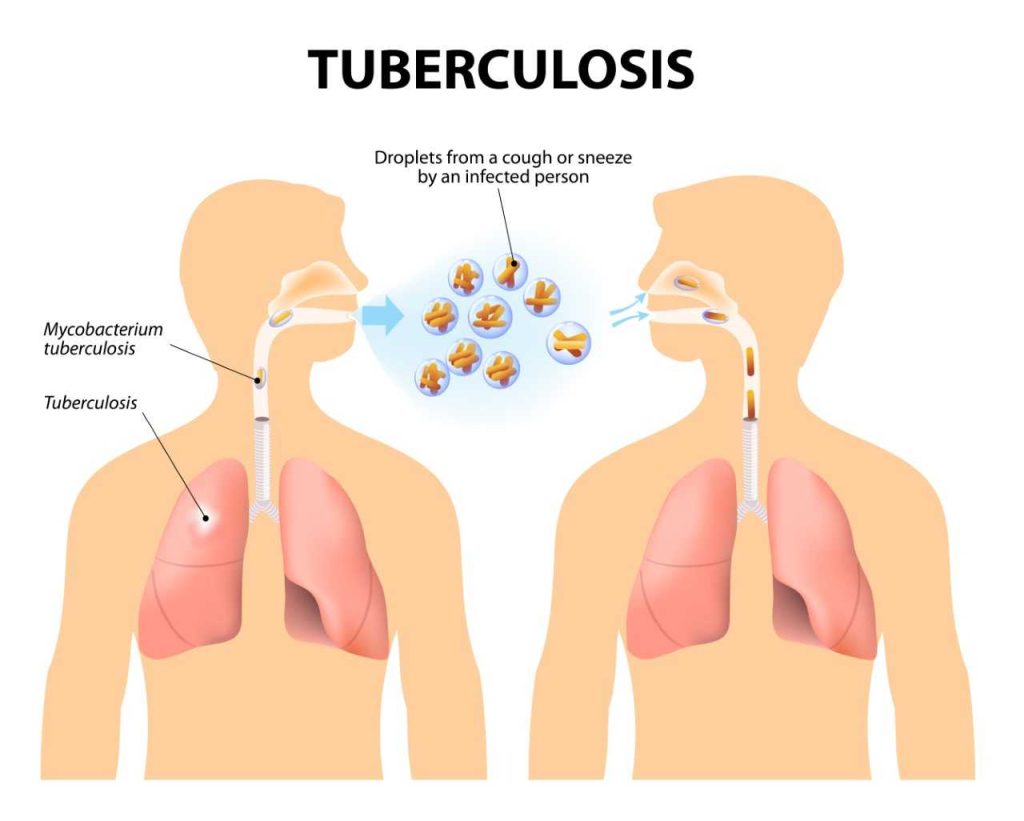
- Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It is an airborne disease, meaning it is spread through the air when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. TB primarily affects the lungs, but can also affect other parts of the body, such as the kidneys, spine, and brain.
- The symptoms of TB include a persistent cough, fever, night sweats, chest pain, fatigue, and weight loss. If the infection spreads to other parts of the body, such as the kidneys, spine, or brain, additional symptoms may be present.
- If left untreated, TB can be fatal. Treatment for TB involves a combination of antibiotics, typically administered over a period of at least 6 months. In some cases, additional medications may be needed.
- To prevent the spread of TB, it is important to practice good hygiene, such as covering your mouth when you cough or sneeze, and washing your hands regularly. It is also important to avoid close contact with anyone who has been diagnosed with TB.
- If you think you may have been exposed to TB, it is important to have a medical evaluation as soon as possible. Early diagnosis and treatment is key to controlling the spread of this disease.
toberculosis, tubarculosis
