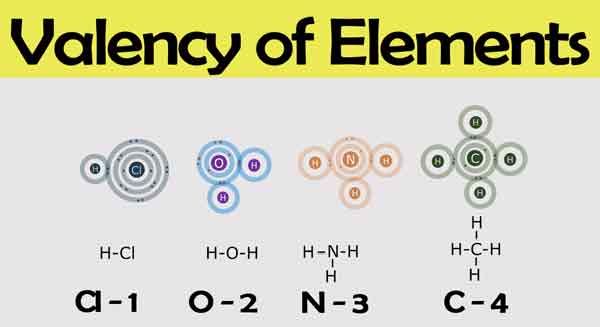
Valency in chemistry is a measure of how many chemical bonds an atom can form. It is related to the number of electrons in the outer shell of an atom, and is determined by the number of protons in the nucleus. For example, Hydrogen has one valence electron and can form one bond, so its valency is 1. Carbon has four valence electrons and can form four bonds, so its valency is 4.
