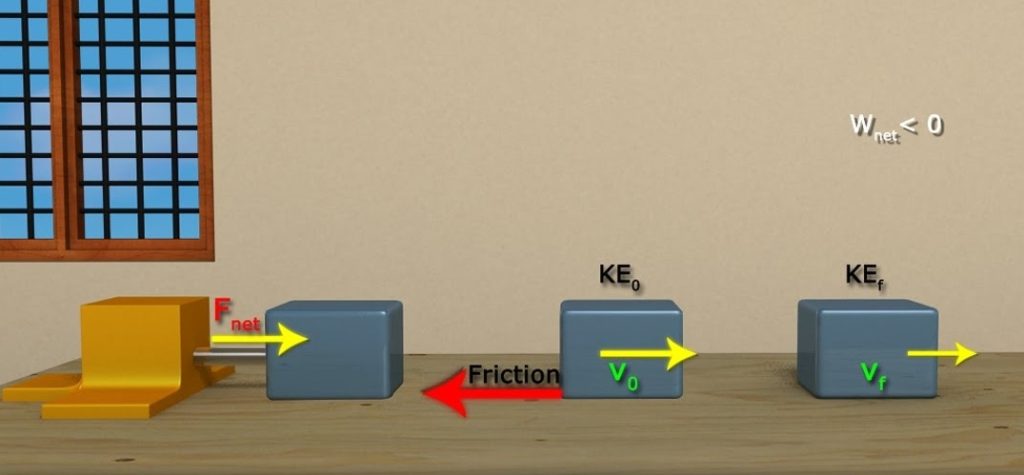
The work-energy principle states that the work done by all forces acting on a particle is equal to the total change in the kinetic energy of the particle. In mathematical terms, this is expressed as:
W = E_k_2 – E_k_1
where W is the work done on the particle, and E_k_1 and E_k_2 are the initial and final kinetic energies of the particle, respectively.
