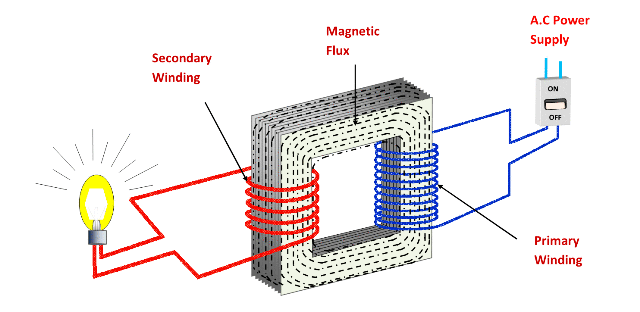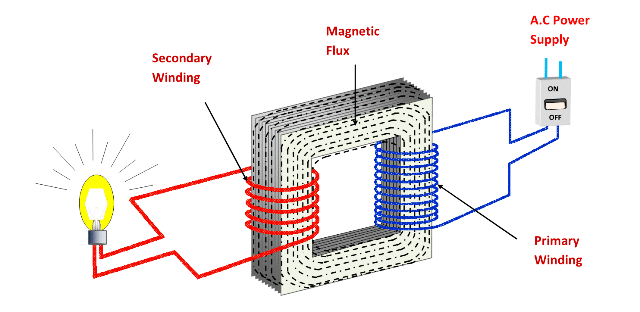
A transformer is an electrical device that is used to transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits through the use of electromagnetic induction. It works by converting the alternating current (AC) in one circuit into another AC of a different voltage level and current. The transformer has two or more separate windings (coils of wire) that are insulated from each other. When an alternating current is applied to one of the windings, it creates a varying magnetic field in the core of the transformer. This field induces a voltage in the other winding, and the two windings become linked. The ratio of the numbers of turns in the two windings determines the ratio of the output voltage to the input voltage. Therefore, transformers are used to increase or decrease the voltage of an AC signal